How Hurricane Trackers Predict Deadly Storms Before They ...
Every year, hurricanes unleash catastrophic damage, yet cutting‑edge hurricane trackers allow meteorologists to forecast a storm’s path, intensity, and landf...
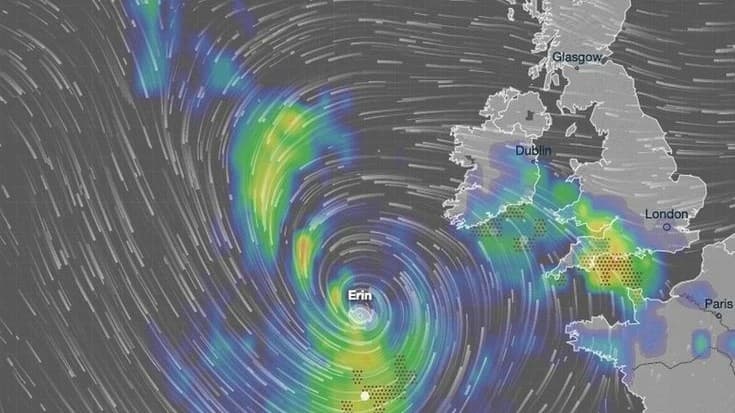
By Dhananjay Singh | Special Report
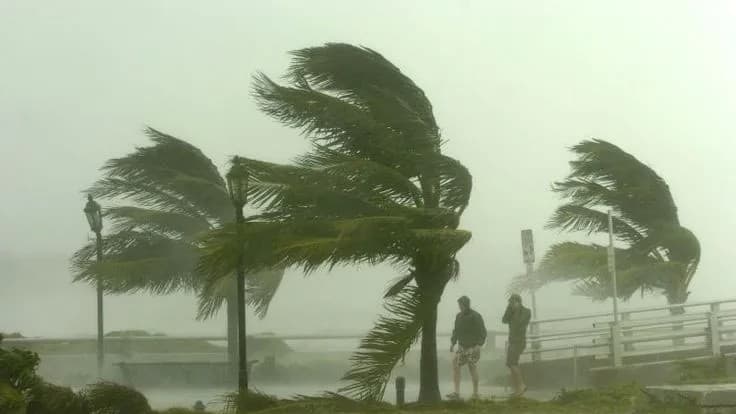
Every year, the world faces the fury of nature in the form of hurricanes, cyclones, and tropical storms. These massive weather systems can destroy everything in their path — homes, power lines, and sometimes, entire cities. But have you ever wondered how meteorologists know when and where a hurricane will strike? How do they predict its path, intensity, and timing days before it makes landfall?
That’s where hurricane trackers come in — the invisible guardians that give us time to prepare, evacuate, and save lives.
🌪️ The Birth of a Hurricane: From Ocean Heat to Chaos
Every hurricane starts its journey over warm ocean waters, typically above 26°C (79°F). The sun heats the surface, causing warm, moist air to rise. As it rises, it cools and condenses, forming clouds and releasing heat — which fuels the storm even more. When wind patterns and pressure conditions are right, this system begins to rotate, creating a powerful vortex: the early stage of a hurricane.
Scientists call this the tropical depression phase. As it strengthens, it becomes a tropical storm, and once its wind speed crosses 74 mph (119 km/h), it earns the title “hurricane.”
🛰️ Watching from the Sky: Satellites as the First Line of Defense
The first people to spot a forming hurricane aren’t on land — they’re in space.
Satellites orbiting Earth, like NOAA’s GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites) or India’s INSAT series, are constantly scanning the oceans. They capture real-time images of cloud formations, temperature, wind speed, and humidity.
From thousands of kilometers above Earth, these satellites can detect the circular cloud patterns that indicate a developing cyclone. Infrared and visible imagery help scientists identify the storm’s center, its rotation speed, and direction.
Each image, sometimes updated every five minutes, is transmitted to ground stations, where meteorologists analyze it. This data becomes the foundation of hurricane tracking.
✈️ Enter the Hurricane Hunters: Flying Into the Storm
Yes, you read that right — some people actually fly into hurricanes.
These are special missions operated by the U.S. Air Force Reserve’s 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron and NOAA’s Hurricane Hunters. These brave pilots and scientists use aircraft equipped with advanced sensors and radars to fly directly into the eye of the storm.
Inside the hurricane, they drop small instruments called dropsondes — tiny weather stations attached to parachutes. As they fall through the storm, they record temperature, humidity, air pressure, and wind speed.
This real, on-site data is crucial. It tells scientists exactly how strong the hurricane is and helps predict its next move with stunning accuracy.
🧠 The Power of Prediction: Computer Models and AI
Once all the satellite and aircraft data is collected, it’s time for the computers to take over — but not like robots, more like intelligent assistants.
Meteorologists feed all this data into forecast models — powerful computer simulations that replicate the atmosphere. These models consider temperature, wind direction, humidity, ocean currents, and even the Earth’s rotation to project the storm’s path.
Some of the most well-known models include:
- GFS (Global Forecast System) – USA
- ECMWF (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) – Europe
- IMD Model – India Meteorological Department
Modern AI tools, including those developed by Google DeepMind, are now helping meteorologists analyze these models faster and more accurately. Instead of relying on manual calculations, AI can compare millions of data points from past storms and provide early warning patterns up to 15 days in advance.
This fusion of human expertise and intelligent modeling has revolutionized how we prepare for hurricanes.
📡 From Data to Decision: How Warnings Reach People
All the gathered information — from satellites, aircraft, and computer models — flows into central forecasting hubs like the National Hurricane Center (NHC) in the United States, IMD (India Meteorological Department) in India, or Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA).
These agencies interpret the data and release official bulletins, which include:
- Storm position and movement
- Wind speed and pressure
- Predicted landfall area
- Timing and intensity forecasts
- Safety and evacuation alerts
From there, news channels, weather apps, and even Google’s alert systems deliver this information directly to the public’s screens.
This is why, days before a storm hits, you start seeing “Hurricane Warning” or “Cyclone Alert” messages on your phone or TV — it’s the final step in the hurricane tracking chain.
🌊 Real-World Example: Hurricane Milton 2025
In October 2025, Hurricane Milton developed over the Caribbean Sea and moved rapidly toward the U.S. Gulf Coast. Within just 72 hours, it intensified from a tropical storm to a Category 4 hurricane.
Thanks to accurate tracking by NOAA satellites and data from Hurricane Hunter missions, forecasts predicted its landfall near Florida with high precision.
Local authorities issued evacuation orders 48 hours before impact, saving thousands of lives.
Even though Milton caused severe flooding and infrastructure damage, the timely tracking and alerts prevented a much higher death toll.
This real-world example proves how crucial hurricane trackers are in disaster management.
⚙️ Behind the Scenes: The Technology That Makes It Work
A hurricane tracker isn’t a single device — it’s a network of technologies working together:
- Satellites – Capture images and temperature maps from space.
- Buoys – Floating sensors in oceans that record water pressure and temperature.
- Radar Stations – Track rainfall and storm movement as it nears land.
- Aircraft Reconnaissance – Collects internal storm data.
- Supercomputers & AI Models – Analyze patterns and generate forecasts.
- Communication Systems – Disseminate warnings through media, apps, and government channels.
Together, they form a global safety web — watching, predicting, and warning humanity before disaster strikes.
🧩 How Accurate Are Hurricane Trackers?
In the early 1980s, hurricane path predictions were often off by hundreds of kilometers. Today, with AI and better models, the margin of error has dropped by nearly 70%.
Modern systems can predict a hurricane’s location three to five days in advance with impressive precision.
However, predicting intensity remains tricky. Sometimes, storms intensify or weaken unexpectedly due to ocean heat or atmospheric changes.
That’s why meteorologists always combine multiple models and keep updating forecasts every few hours.
🧭 The Role of Public Awareness and Preparedness
Technology can only do so much — the rest depends on how people respond.
Public awareness campaigns, early evacuation plans, and local community drills are essential.
Countries like the U.S., Japan, and India have built disaster response frameworks that rely directly on hurricane tracker data to coordinate rescue operations.
Apps like Google Weather, Windy, and IMD Mausam now provide real-time tracking and alerts in local languages, making this life-saving information accessible to everyone.
🧭 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a hurricane tracker?
A hurricane tracker is a system that uses satellites, radars, aircraft, and computer models to monitor and predict the path and strength of hurricanes. It helps meteorologists and government agencies issue timely warnings to protect people and property.
2. How do scientists track hurricanes?
Scientists track hurricanes using weather satellites, ocean buoys, radar systems, and aircraft called Hurricane Hunters. These tools collect real-time data on wind speed, temperature, pressure, and storm direction. The information is analyzed by computer models to predict where the hurricane will move next.
3. What technology is used in hurricane tracking?
Hurricane tracking combines satellite imaging, AI-powered forecasting models, radar systems, and supercomputers. Together, they analyze billions of data points to predict storm paths and intensities with high accuracy.
4. Can AI really predict hurricanes accurately?
Yes. Artificial Intelligence is now being used to improve forecasting accuracy. AI models, such as those developed by Google DeepMind, analyze historical weather data and live satellite feeds to predict hurricane movement up to 15 days in advance — faster and often more accurate than traditional methods.
5. Who provides official hurricane updates?
Official updates come from organizations like the National Hurricane Center (NHC) in the U.S., the India Meteorological Department (IMD), and the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). They monitor global storm activity and issue alerts for affected regions.
6. How do hurricane warnings reach the public?
Once a storm’s path is confirmed, alerts are shared via TV news, radio, weather apps, and mobile notifications. Google and Apple also send real-time storm alerts based on your location, ensuring people can evacuate or prepare on time.
7. Why do some hurricane predictions change suddenly?
Hurricanes can intensify or weaken quickly due to sea temperature changes or atmospheric conditions. This is why meteorologists constantly update forecasts every few hours to provide the latest and most accurate information.
8. How can people stay safe during a hurricane?
Follow evacuation orders, stay updated through official weather channels, keep emergency supplies ready, and avoid traveling during storm alerts. Knowing your local shelters and safety plans can save lives.
9. What is the difference between a hurricane, cyclone, and typhoon?
They’re all the same type of storm — a tropical cyclone. The name changes based on the region: “Hurricane” in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific, “Cyclone” in the Indian Ocean, and “Typhoon” in the Northwest Pacific.
10. What’s the future of hurricane tracking?
The future involves smarter AI systems, faster satellites, and real-time ocean sensors that can detect changes instantly. These innovations will make forecasting even more accurate and life-saving in the coming years.
Dhananjay Singh
Professional Content Writer, Researcher & Visionary Storyteller
"तरक्की को चाहिए नया नज़रिया—और यह नज़रिया शब्दों से शुरू होता है।"
More from Dhananjay Singh →

